Which option would you pick?
- Growth Initiative A: Gains you 300 new users this week, but no additional growth afterward.
- Growth Initiative B: Starts with 15 new users in week one, increases by 15% every week (17 in week 2, 19 in week 3, etc.), and continues growing at that rate indefinitely.
While Initiative B will take 20 weeks to reach 300 users, after 1 year, you’ll have accumulated 43,196 new users, and your weekly growth will be around 3,500 new users. By the end of year two, you could have 11,451,393 new users—assuming the 15% weekly growth holds.
What is a Growth Loop?
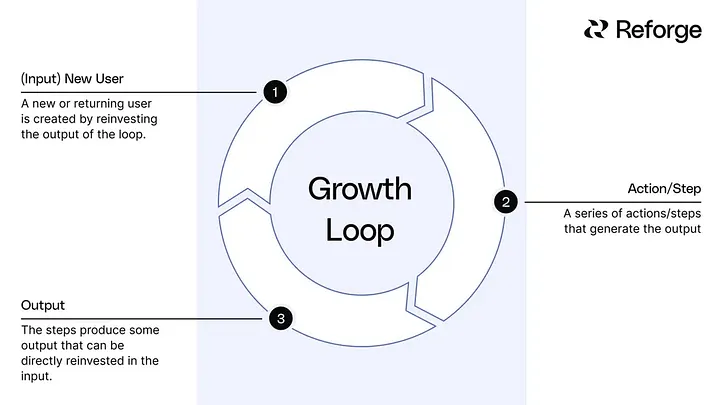
A growth loop is a self-sustaining marketing model designed to generate continuous growth for a product or business.
Unlike traditional, linear models like the marketing funnel, which guides potential customers from awareness through to conversion, growth loops work in a circular, iterative manner. The output of one cycle feeds into the next, creating a loop that can scale and lead to exponential growth when executed well.
Growth Loops vs. Funnels
Traditionally, marketers have used models like the AARRR framework to understand customer journeys and growth.
Here’s a quick comparison of growth loops vs. funnels:
| Aspect | Growth Loop | Funnel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A self-reinforcing cycle where the output feeds the next cycle. | A linear process that moves potential customers through stages from awareness to conversion. |
| Focus | Encourages repeat engagement and virality to drive growth. | Focuses on moving customers through stages toward conversion. |
| Structure | Circular, iterative, ongoing process. | Linear, one-way flow from start to finish. |
| Customer Journey | Emphasizes engagement, retention, and viral growth. | Primarily focuses on acquiring new customers and converting them. |
Ready to optimize your marketing and sales funnels? Contact us today for strategies and tools that will help you attract, engage, and convert leads faster than ever before!
The 4 Main Types of Growth Loops
There are four primary types of growth loops: the viral loop, user-generated content loop, paid marketing loop, and sales loop.
1. Viral Growth Loop
A viral growth loop relies on users bringing in more users through sharing and referrals.
How it works:
- A percentage of users who sign up invite their friends.
- A percentage of invitees click on the invitation link.
- A percentage of those who click sign up as new users.
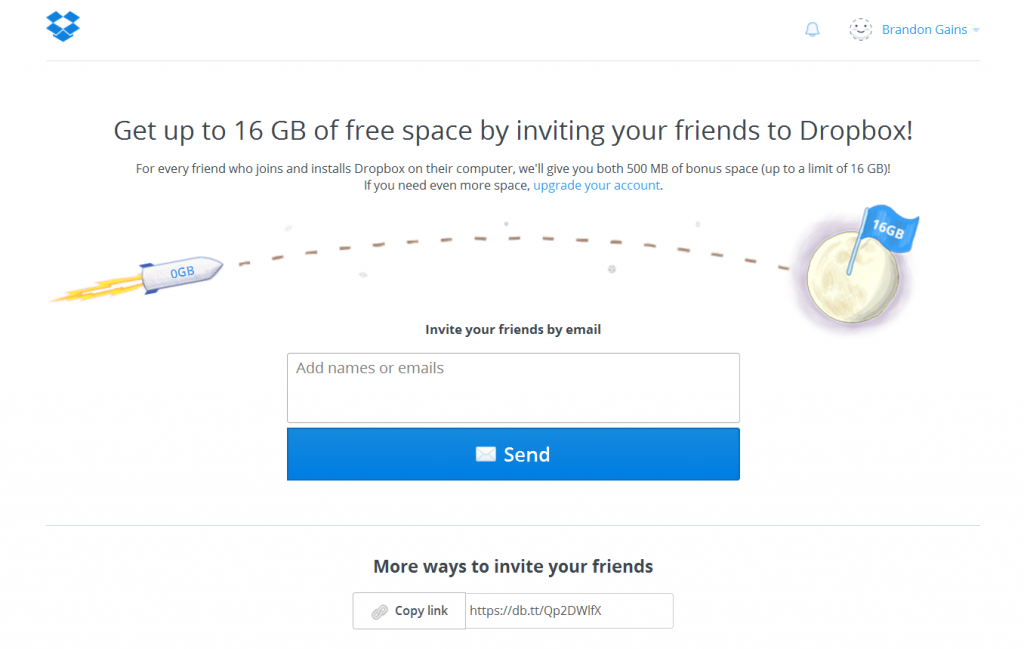
Companies using viral loops: LinkedIn, Slack, Dropbox, Instagram.
2. UGC (User-Generated Content) Growth Loop
In a UGC growth loop, user-created content drives engagement and attracts new users, perpetuating further content creation.
How it works:
- New users sign up.
- A percentage of them create content.
- Google indexes that content.
- New users discover that content via search and sign up.
Companies using UGC loops: Houzz, Pinterest, Moz, Yelp.
3. Paid Marketing Growth Loop
A paid marketing loop involves reinvesting revenue from acquired customers into paid advertising, which drives more customer acquisition and revenue.
How it works:
- User signs up.
- A percentage of users make a payment.
- Revenue from these payments is reinvested into ads.
- A portion of the ad audience engages, creating more ad spend.
Companies using paid marketing loops: Clash of Clans, Uber, SurveyMonkey, Dollar Shave Club.
4. Sales Growth Loop
A sales growth loop is a cyclical process where successful sales generate customer referrals and repeat business, fueling further growth.
How it works:
- A new customer signs up.
- The company uses customer profiles to recruit more sales reps.
- More reps lead to more customers over time.
Companies using sales loops: HubSpot, Zendesk, Box, New Relic.
Growth Loops & Retention
Retention is critical for the success of growth loops. Small improvements in retention can significantly boost engagement and the effectiveness of these loops.
Here’s how retention impacts different types of growth loops:
- Viral Loops: Longer retention means more viral touchpoints and higher chances of users participating in the viral acquisition loop.
- UGC Loops: Better retention results in more content being created, leading to more content being indexed by search engines, which brings in new users.
- Paid Marketing Loops: Retaining users means more revenue to reinvest in advertising, which drives further growth.
- Sales Loops: Higher retention rates lead to a bigger pool of customers, fueling more sales rep recruitment, which in turn attracts even more customers.
B2B Growth Loops
Dropbox is a classic example of an effective B2B growth loop. Here’s how it works:
- A user signs up for Dropbox.
- The user shares a document with others.
- The recipients click on the link and access the document.
- Some of those recipients become new Dropbox users.
Key Takeaway
Rather than relying on one-off marketing tactics, your focus should be on building initiatives that can compound and yield sustainable results over time. Growth loops are all about creating cycles that self-perpetuate and drive ongoing growth, often resulting in much larger gains than linear models.

Leave a Reply